Unveiling the Hidden Connection: Decoding the Role of DAO Enzyme in Dermatitis Herpetiformis
Dermatitis Herpetiformis (DH) is a chronic and troubling autoimmune skin disease closely linked to celiac disease (P- problem). In this article, we’ll take an in-depth look at what it is and how it relates to DAO enzymes.
What is Dermatitis Herpetiformis?
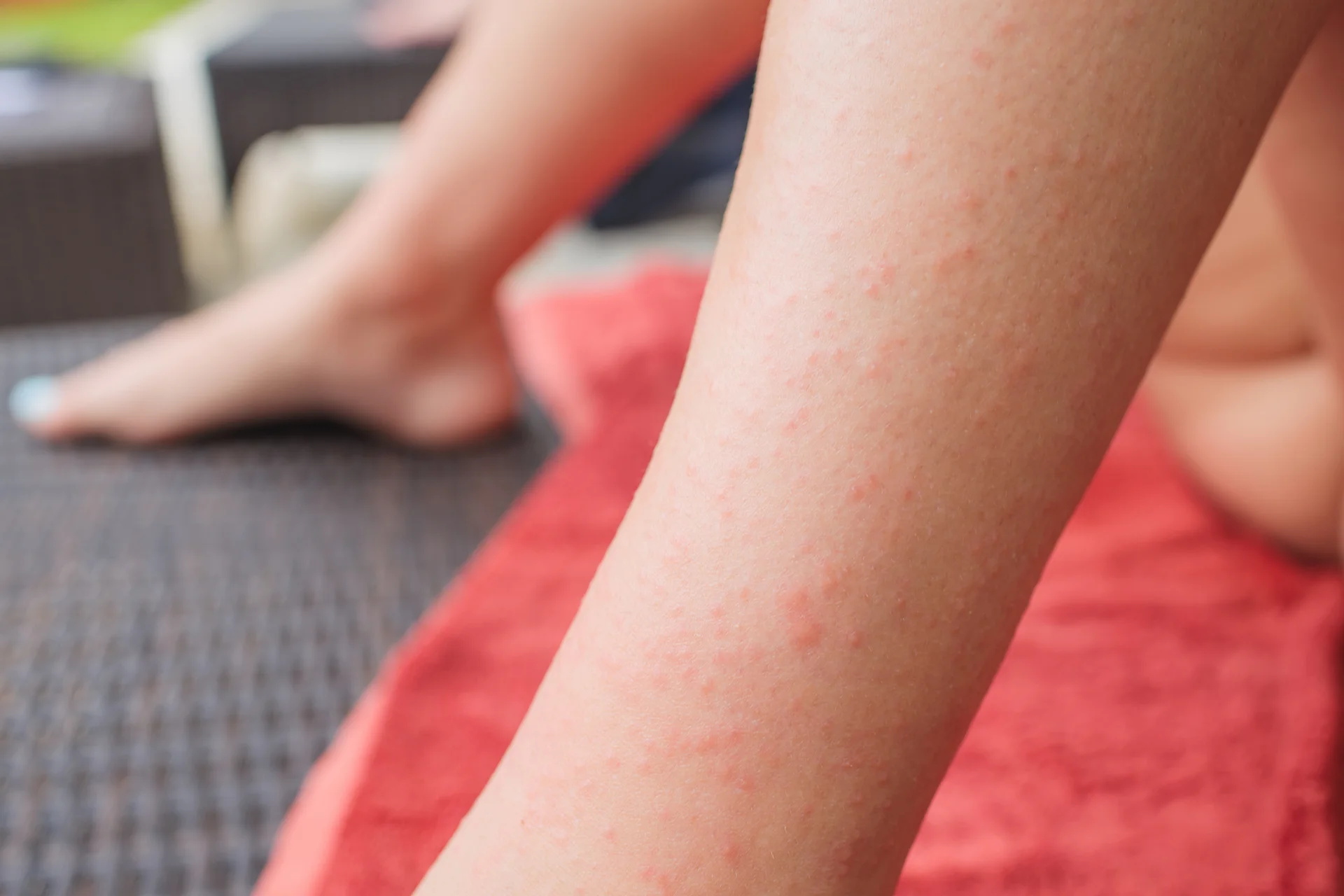
Dermatitis Herpetiformis is a skin condition that is closely related to histamine intolerance and gluten sensitivity. It is an autoimmune disorder that affects the skin and is caused by the immune system’s response to gluten consumption. The disease manifests itself through itchy and painful red rashes that turn into blisters on the skin.
Histamine intolerance is a common issue among individuals with Dermatitis Herpetiformis. The release of histamine triggers a cascade of events in the body, leading to a massive immune response, which then causes the formation of these rashes.
The symptoms of Dermatitis Herpetiformis include intense itching, a burning and stinging sensation, red and inflamed bumps on the skin, and the formation of blisters that fill with fluid. These blisters can break open, leading to oozing and crusting of the skin. The disease often affects the elbows, knees, buttocks, scalp, and back.
The exact causes of Dermatitis Herpetiformis are not yet fully understood. However, there are several possible factors that may contribute to the development of the disease.
These include:
- Genetic factors,
- Environmental triggers
- Dietary habits that involve the consumption of gluten-containing foods.
Individuals that develop Dermatitis Herpetiformis often experience a heightened response to food antigens such as gluten, which trigger the release of histamine and other inflammatory substances. Those with the disease may benefit from a gluten-free diet, which can lead to a significant reduction in symptoms and the severity of the rash.
What is DAO Enzyme?
DAO (diamine oxidase) enzyme is a digestive enzyme that is primarily produced in the lining of the small intestine. Its crucial role is to break down histamine, a compound that is produced by the body, and is also present in some foods.
Histamine is a neurotransmitter that helps in regulating the immune response and is responsible for several physiological functions in the body. DAO enzyme plays a crucial role in metabolizing histamine, preventing its excess accumulation and subsequent symptoms of histamine intolerance.
Individuals who have low levels of DAO enzyme can develop histamine intolerance. Histamine intolerance is a condition where the body is unable to break down histamine properly, leading to several symptoms, including skin inflammation, chronic inflammation, irritable bowel syndrome, and gastrointestinal issues.
Several factors can impact the production and activity of DAO enzyme, including leaky gut syndrome, autoimmune diseases, and genetic factors. Furthermore, consuming foods that are high in histamine or those that trigger the release of histamine can also interfere with DAO activity, exacerbating the symptoms of histamine intolerance.
To address this issue, several options can be pursued.
| Option | Description |
| Histamine blockade | Individuals can supplement with DAO enzyme or other nutrients that support histamine breakdown, such as vitamin C. |
| Supplementation with DAO enzyme or histamine-blocking agents | Helps individuals manage the symptoms of histamine intolerance. |
| Low-histamine diet | Focusing on foods that are low in histamine can reduce the histamine load on the body and contribute to managing the symptoms of histamine intolerance. |
Causes of Dermatitis Herpetiformis
Dermatitis Herpetiformis (DH) is a chronic skin condition that manifests in the form of itching and blistering. It is often associated with gluten intolerance and celiac disease, but the causes of DH are still not fully understood.
Various factors may contribute to the development of DH, including genetic factors, environmental factors, and diet and lifestyle. In this section, we will discuss each of these factors in detail to provide a better understanding of the causes of DH.
Genetic Factors
Genetics is one of the factors that plays a critical role in the development of dermatitis Herpetiformis (DH). Understanding the genetic factors responsible for DH is critical for identifying individuals who are at risk of developing the condition.
Several genes have been implicated in the development of DH, with the two most often associated with the HLA (Human Leukocyte Antigen) system being HLA-DQ2 and HLA-DQ8. Genes in this system affect immune system function. HLA-DQ2 is present in approximately 90% of people with celiac disease, and a majority of people with DH also possess it. HLA-DQ8 is also less commonly found in people with DH and celiac disease.
In people with DH who have the HLA-DQ2 and/or HLA-DQ8 genes, the immune system responds abnormally to gluten, and this overactive immune response leads to the development of skin inflammation and blisters.
The immune system recognizes gluten as a foreign body and attacks it, mistaking it for a harmful pathogen. During this misguided attack, toxic antibodies build up, causing an inflammatory reaction that damages the skin, causing the characteristic blistering and itching associated with DH.
Moreover, cross-reactivity could also contribute to the development of DH. In some cases, individuals with DH may generate antibodies against tissue in the body that have similarities to gluten proteins.
This situation results in a phenomenon referred to as “cross-reactivity“. Cross-reactivity can lead to the immune system mistakenly attacking and damaging healthy tissue, leading to skin inflammation and chronic inflammation throughout the body.
Environmental Factors
Apart from genetic factors, environmental factors are also known to contribute to the development and aggravation of dermatitis Herpetiformis (DH). Heavy metal toxicity and histamine intolerance are two environmental factors that have been linked to this autoimmune skin disease.
Heavy metal toxicity occurs when excessive amounts of heavy metals like lead, mercury, and arsenic accumulate in the body, leading to a range of health problems.
Studies have shown that heavy metal toxicity can cause skin inflammation and aggravate autoimmune disorders like DH. Similarly, histamine intolerance is a condition where the body cannot effectively break down histamine, leading to an overabundance that causes skin inflammation and itchiness.
Aside from heavy metal toxicity and histamine intolerance, certain environmental triggers like exposure to pollutants, stress, certain medications, and infections may also contribute to the development of DH.
For instance, exposure to pollutants like pesticides and chemicals can trigger an immune response that leads to skin inflammation and irritation. Stress, on the other hand, can cause an imbalance in the immune system, leading to flare-ups of DH. Certain medications, such as NSAIDs and antibiotics, have also been known to trigger DH, while infections can cause an immune response that damages the skin and leads to inflammation.
Diet and Lifestyle

Diet and lifestyle modifications play an important role in managing dermatitis Herpetiformis (DH). While there is no specific diet that can cure DH, research suggests that following a Mediterranean diet can be beneficial due to its anti-inflammatory effects.
It’s also important to avoid foods high in histamine. Common high histamine foods include aged cheeses, cured meats, pickled and fermented foods, and alcohol. To further reduce histamine levels in food, boiling is a better cooking method than roasting or BBQing.
Some DH patients may also benefit from following a low oxalate or a low FODMAP diet. A low oxalate diet aims to reduce the consumption of foods high in oxalates, such as spinach, rhubarb, and nuts, as oxalates can exacerbate DH symptoms in some individuals.
Similarly, the low FODMAP diet aims to reduce the consumption of certain carbohydrates, which can lead to symptoms such as bloating, gas, and abdominal pain.
Incorporating these dietary modifications and making healthier lifestyle choices can help manage DH symptoms and improve overall health. By adopting a Mediterranean-style diet, avoiding high histamine foods, and potentially following a low oxalate or low FODMAP diet, DH patients can further reduce inflammation and improve their quality of life.
Symptoms of Dermatitis Herpetiformis
Dermatitis Herpetiformis (DH) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the skin. It is characterized by the presence of itchy, blistering rashes on the elbows, knees, scalp, and buttocks, among other areas. These rashes are often symmetrical, and can vary in size and shape.
DH can also cause intense itching and a burning sensation in affected areas. Other symptoms of DH include gastrointestinal symptoms like abdominal pain, bloating, and diarrhea, as well as joint pain and fatigue. In this section, we will explore the various symptoms of DH in more detail.
Skin Rashes and Blisters
Skin rashes and blisters are common symptoms of dermatitis Herpetiformis. These rashes and blisters develop symmetrically, often on the elbows, knees, buttocks, and scalp, but can also occur on the face, hairline, and neck. The blisters are small and grouped together, containing clear or cloudy fluid that may become infected if scratched.
Patients with dermatitis Herpetiformis may experience a burning or stinging sensation that takes a few days to a few weeks to heal and can leave behind dark spots or scars. It is important for patients to avoid scratching the affected areas to prevent infections.
Triggers of Skin Rashes and Blisters
The most common triggers of skin rashes and blisters associated with dermatitis Herpetiformis are the consumption of gluten-containing foods or exposure to iodine. Gluten is a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye, and can be hidden in many foods and products. Iodine is a mineral found in seafood, eggs, dairy products, and some medications.
Treatment Options for Skin Rashes and Blisters
There are different treatment options for skin rashes and blisters caused by dermatitis Herpetiformis:
| Treatment Options | Description |
| Elimination Diet | Avoiding gluten and iodine-containing foods can help manage symptoms of skin rashes and blisters caused by dermatitis Herpetiformis. It is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to develop an appropriate dietary plan. |
| Topical Corticosteroids | Application of corticosteroid creams can reduce inflammation and itching in affected areas, providing relief from skin rashes and blisters caused by dermatitis Herpetiformis. |
| Medications that Block Histamine Release or Reduce Immune Response | Other medications that block histamine release or reduce the immune response may be prescribed to patients with dermatitis Herpetiformis to alleviate symptoms associated with skin rashes and blisters. |
| Skincare Practices | Improving skin health and reducing symptoms can be achieved by using gentle, fragrance-free skincare products and avoiding hot water or harsh chemicals, which can exacerbate skin rashes and blisters. This contributes to overall management of dermatitis Herpetiformis symptoms. |
Itching and Burning Sensation
Itching and burning sensations are two of the most commonly reported symptoms among individuals with dermatitis Herpetiformis. These sensations can range in intensity and may be most severe in areas where rashes or blisters are present. However, it is important to recognize that these sensations are not always caused by external factors, like irritants or allergens.
In fact, itching and burning sensations associated with dermatitis Herpetiformis are often a result of the underlying autoimmune response that characterizes the condition. This autoimmune response leads to the accumulation of immune cells in the skin, which can cause inflammation and the release of histamine and other chemical mediators that contribute to itching and burning sensations.
To manage these symptoms effectively, it is important for individuals with dermatitis Herpetiformis to identify triggers that may exacerbate their condition. Common triggers include the consumption of gluten-containing foods and exposure to iodine, as well as stress, infection, and hormonal changes.
Individuals with dermatitis Herpetiformis may also benefit from implementing various lifestyle changes and therapies that can help reduce inflammation and histamine levels in the body. This may include following a gluten-free diet, supplementing with vitamin C, using topical or oral medications that block histamine release or reduce immune response, and avoiding harsh chemicals or irritants that can exacerbate symptoms.
Other Symptoms
Histamine intolerance is a condition characterized by an overload of histamine in the body, leading to a range of symptoms. However, it can be a challenging condition to diagnose due to the wide variety of symptoms that can mimic other conditions.
Other symptoms reported by individuals with histamine intolerance include respiratory symptoms, gastrointestinal symptoms, nervous system symptoms, and circulatory system symptoms.
Respiratory symptoms such as dyspnea (difficulty breathing) and wheezing may be present in individuals with histamine intolerance. However, these symptoms are also common in conditions such as asthma and bronchitis. Therefore, it is important to rule out these conditions before making a diagnosis of histamine intolerance.
Gastrointestinal symptoms such as bloating, abdominal pain and discomfort, and constipation may also be present in individuals with histamine intolerance. These symptoms can be similar to those of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and other digestive disorders. Careful evaluation and diagnosis are necessary to differentiate between these conditions.
Nervous system symptoms like headaches, migraines, and dizziness can also be present in individuals with histamine intolerance. These symptoms can also be present in conditions such as vestibular disorders, like vertigo, and neurological conditions such as multiple sclerosis. Thorough evaluation and diagnosis are necessary to determine if histamine intolerance is the underlying cause or if it is a symptom of another condition.
Circulatory system symptoms like hypotonia (low blood pressure) and tachycardia (rapid heart rate) may also occur as a result of histamine intolerance. However, these symptoms can also be present in conditions such as postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS). It is important to consider all possible conditions and conduct appropriate testing to determine the underlying cause of these symptoms.
Reproductive system symptoms have also been reported in some individuals with histamine intolerance, including menstrual cramps and irregular periods. However, these symptoms can also be attributed to various gynecological conditions. Therefore, it is important to consider all symptoms and conduct proper diagnostic tests before concluding that histamine intolerance is the underlying cause.
It is important to recognize that histamine intolerance can be challenging to diagnose due to the wide range of symptoms that can overlap with other conditions. Thorough evaluation and consideration of all symptoms are necessary to differentiate histamine intolerance from other conditions and establish an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnosis of Dermatitis Herpetiformis
Diagnosing Dermatitis Herpetiformis (DH) can be challenging due to its range of presentations, just like Celiac Disease. However, there are several diagnostic procedures that can help identify the condition.
A skin biopsy test is considered the most reliable method of diagnosing DH. During a biopsy, a small sample of skin is removed from the area near a blister or rash. The sample is then stained and checked for the presence of IgA antibodies and complement protein C3. The presence of these antibodies is a strong indicator of DH.
Blood tests may also be ordered to confirm the presence of IgA antibodies and complement protein C3. However, they are less reliable than biopsy results. In some cases, a trial of a gluten-free diet can also be used as a diagnostic tool for DH. If the patient’s symptoms improve on a gluten-free diet, this strongly suggests DH.
It is crucial to establish an accurate diagnosis of DH to avoid misdiagnosis and unnecessary treatment. Misdiagnosis can lead to delays in appropriate treatment and unnecessary exposure to gluten-free diets or drugs that may have harmful side effects. Therefore, it is essential to consider all diagnostic tools available and work with a healthcare provider experienced in treating DH to ensure the most effective diagnostic plan is implemented.
Skin Biopsy Test
To establish an accurate diagnosis of Dermatitis Herpetiformis (DH), medical professionals often turn to a skin biopsy test. This test involves removing a small piece of skin tissue from the affected area and examining it closely under a microscope for any changes in the skin layers.
Before the biopsy is taken, a local anesthetic is applied to the area to ensure that the patient is comfortable throughout the procedure. The biopsy itself generally takes around 10 to 15 minutes to complete and may cause minor discomfort, such as a slight stinging or burning sensation.
Medical professionals may also perform blood tests to detect the presence of specific antibodies, such as immunoglobulin A (IgA) antibodies and complement protein C3. These serological tests can help provide additional evidence to support the diagnosis of DH.
Overall, the skin biopsy test is a crucial diagnostic tool in identifying Dermatitis Herpetiformis and should not be overlooked. If you are experiencing symptoms of DH, it is important to work with a healthcare provider experienced in treating the condition and to consider all diagnostic tools available to ensure the most accurate diagnosis possible.
Treatment for Dermatitis Herpetiformis
Dermatitis Herpetiformis (DH) is a chronic skin condition that can be uncomfortable and difficult to manage. While the most effective treatment for DH is a gluten-free diet, medical professionals may also prescribe oral medications to help manage symptoms and promote healing. These medications can help to reduce inflammation, control the immune response, and prevent further damage to the skin. In this section, we will discuss some of the most common oral medications used to treat Dermatitis Herpetiformis.
Oral Medications
There are several oral medications that can be used to treat dermatitis Herpetiformis (DH). One of the most common types of oral medication prescribed for DH are Sulphones. Sulphones work by targeting the bacteria that cause skin inflammation. They are typically taken once a day and can be quite effective in managing DH symptoms.
Dapsone is another oral medication that can be used to treat DH. This medication has been shown to reduce inflammation and prevent further skin damage in patients with DH.
It works by inhibiting the production of an enzyme called dihydrofolic acid reductase, which is involved in the synthesis of DNA and RNA. Dapsone is typically taken once a day and it can take several weeks for patients to see improvement in their symptoms.
Although these oral medications can be effective in treating DH, patients should be aware of the potential side effects. Sulphones can cause nausea, dizziness, and headaches. In rare cases, they can also cause liver damage or allergic reactions. Dapsone can cause similar side effects as well as a drop in white blood cell count and anemia. Patients should discuss these potential side effects with their doctor prior to starting treatment.
It is important for patients with DH to work closely with their medical provider to determine the best course of treatment. While oral medications can be effective, they are not suitable for everyone. In some cases, a gluten-free diet may offer significant improvement in DH symptoms. In other cases, alternative therapies may be recommended. With proper treatment and management, patients with DH can find relief from their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Sulfones
Sulfones, such as Dapsone, are commonly used in the treatment of Dermatitis Herpetiformis (DH), a skin condition typically associated with celiac disease. These medications work by targeting the bacteria that cause skin inflammation and reducing the production of an enzyme involved in DNA and RNA synthesis in the body.
The mechanism of action for sulfones in reducing symptoms of dermatitis Herpetiformis involves the inhibition of dihydrofolic acid reductase, an enzyme necessary for the production of new cells in the body. By blocking this enzyme, sulfones can reduce inflammation and prevent further skin damage in patients with DH.
While sulfones can be effective in treating DH, patients should be aware of potential side effects. These may include nausea, dizziness, and headaches. In rare cases, they can also cause liver damage or allergic reactions.
Moreover, patients with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency should not take sulfones as this can cause hemolytic anemia. It is best to discuss the use of sulfones with your medical provider to assess your risk factors for these and any other side effects and contraindications.
Dietary and supplemental recommendations may support the use of sulfones in managing DH symptoms. Increasing sulfur intake through foods such as fermented cruciferous vegetables, increasing pantothenic acid intake through foods such as organ meats and dairy products, and increasing selenium intake through foods such as seafood and Brazil nuts may help support skin health and reduce inflammation.
These nutrients can be found in a wide variety of foods and can be obtained through dietary changes or supplementation under the guidance of a healthcare practitioner.
Intrigued by the intricate relationship between DAO Enzyme and Dermatitis Herpetiformis?
Dive deeper into this fascinating topic and explore potential solutions at SeeBeyond Shop. Take the next step towards understanding and managing this enigmatic skin condition.
Visit SeeBeyond Shop today!