How Understanding Diamine Oxidase Foods Can Improve Your Quality of Life
Curious if you ever feel bloated, itchy, or just ” off ” after a meal but can’t quite pinpoint why?
You may be one of the millions suffering from undiagnosed histamine intolerance. Histamine is found naturally in many foods and is usually broken down by an enzyme called diamine oxidase (DAO).
However, if you have low DAO levels or other conditions impairing histamine metabolism, eating histamine-rich foods can lead to unpleasant symptoms.
The good news? Histamine intolerance is manageable through diet and lifestyle changes. By identifying high-histamine triggers and focusing on foods that boost your DAO, you can find relief from symptoms and get back to enjoying meals again.
Dietary adjustments, like following a low-FODMAP or homemade elimination diet, can help uncover your personal triggers. Supplementing with DAO-boosting enzymes and probiotics also provides extra support for processing any histamines you do consume.
While managing histamine intolerance requires commitment, the benefits of reduced discomfort, improved digestion, and an enhanced relationship with food make it worth it. With time and consistency, you’ll be on the path to symptom-free living and unlocking the secrets to histamine intolerance relief.
Ready to get started? Let’s dive into how an optimized diet and trusted remedies can help you feel better today!
| Don’t let histamine intolerance control your life. Book a visit with SeeBeyond Medicine to learn about the benefits of DAO Foods and start feeling better. |
The Science Behind Histamine Intolerance
Histamine is one of several biogenic amines produced naturally in the body and found in trace amounts in foods. As a neurotransmitter, histamine helps regulate many essential functions like blood pressure, inflammation, and digestion. It works by activating various histamine receptors, especially those lining your digestive tract and intestines.
Inadequate levels of the enzymes needed to break down histamine, such as diamine oxidase (DAO) and histamine N-methyltransferase, can lead to symptoms of intolerance. Genetics, disease, small intestine bacterial overgrowth, and other factors can all contribute to decreased enzyme activity over time. With lower histamine degradation, more is left to activate receptors, resulting in uncomfortable side effects.
DAO, in particular, helps break down a large percentage of dietary and bodily histamines before they reach the bloodstream. Issues that compromise DAO production or reduce its effectiveness, such as a decades’ worth of digestive inflammation or SIBO, allow excess histamine to build up and spread throughout your body.
This biochemical imbalance ultimately leads to the constellation of signs like digestive distress, skin irritation, joint pain, and cognitive difficulties associated with histamine intolerance.
While real progress has been made in recognizing histamine intolerance, much remains unknown about its mechanisms and complex relationships.
Ongoing research continues to shed more light on how to best regulate all compounds involved in histamine handling and support optimal health.
Through diet, lifestyle enhancements, and as-needed supplementation though, you absolutely can gain control of symptoms and live vibrantly despite any known or unknown limitations in histamine degradation.
Recognizing Histamine Intolerance Symptoms
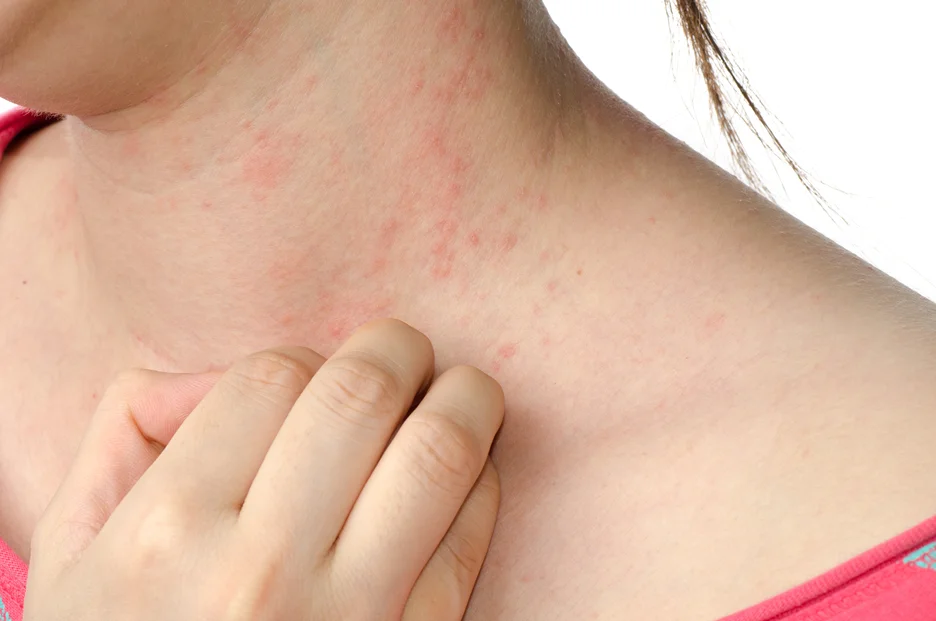
Have you ever noticed a pattern of unpleasant yet seemingly unrelated symptoms that you can’t quite shake? If so, there’s a chance histamine intolerance could be to blame. Some of the most common symptoms of histamine intolerance include:
- Nasal congestion or sinus irritation: Excess amounts of histamine is linked to runny nose, sneezing, and nasal inflammation.
- Digestive distress: Digestive issues like bloating, cramping, diarrhea, or constipation are frequently reported. Burping, gas, and abdominal pain can also occur after eating trigger foods.
- Skin allergic reactions: Itching, hives, eczema flare-ups, and dermatitis point to a histamine overload in sensitive individuals. Oral allergy syndrome may develop over time.
- Joint pain or inflammation: For those with mast cell activation syndrome, excess histamine can accumulate in joints and soft tissues, leading to pain, swelling, and stiffness.
- Cognitive difficulties: Impairments in focus, concentration, and memory are possible due to histamine’s impact on brain function. Headaches can also develop.
Several conditions have been linked to increased histamine levels and a higher risk of intolerance, including inflammatory bowel diseases, irritable bowel syndrome, and mast cell activation syndrome.
If you experience clusters of symptoms that concern you, consulting your doctor is critical. They can evaluate your health history, run targeted tests when needed, and may refer you to specialists such as a gastroenterologist, allergist, or immunologist.
Managing underlying conditions, controlling inflammation, balancing gut bacteria, removing triggers, and supporting detoxification and digestion may all be recommended. A willingness to learn and adjust makes overcoming symptoms possible in even the most challenging cases.
| Don’t let histamine intolerance control your life. Book a visit with SeeBeyond Medicine to learn about the benefits of DAO Foods and start feeling better. |
Histamine-Rich Foods and Their Effects
Many foods contain natural histamines, especially protein-rich and fermented varieties. However, too much of a good thing leads to trouble for those with intolerance. Some of the top histamine offenders include:
- Fresh and pre-cut produce: Leafy greens, tomatoes, spinach, broccoli, and Brussels sprouts pack the most histamines. Cortisol or epinephrine sensitivities can make these trigger symptoms at any time.
- Fermented foods: Yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, miso, tempeh, natto, and chili pastes are high in histamines due to fermentation.
- Dried or canned fish: Tuna, sardines, mackerel, anchovies, herring, and salmon contain the amino acids needed to produce histamine. Canned fish tends to be worse due to preservatives added during processing.
- Meat and poultry: Bacon, sausage, salami, prosciutto, pepperoni, and canned beans are common problem foods.
- Alcohol: Especially red wine, but also beer, liquor, and mixes contain compounds that can aggravate histamine receptors
- Artificial additives: MSG, BPA, sulfites, and synthetic colorings may promote excess histamine production or impair breakdown. They are found in many packaged and preserved foods.
Too much histamine in the diet can lead to toxicity, sensitivity, and exacerbation of underlying conditions. For those with inflammatory and autoimmune disorders, high histamine loads essentially add insult to injury. Digestive issues like SIBO may also develop over time due to a disruption in gut bacteria or impaired enzymatic ability to handle histamines properly.
An elimination diet removing common triggers is the basis for effective management. Once symptoms have improved, slowly reintroducing foods one by one helps gain clarity on your personal tolerance levels and limits. With awareness of both histamine content and sensitivity, delicious and balanced home cooking using fresh, whole ingredients becomes possible.
Dietary Strategies for Managing Histamine Intolerance
To effectively manage histamine intolerance, adopting a low-histamine diet is key. This means reducing high-histamine foods and moderating even moderate sources to prevent excess buildup. Some essential strategies include:
Avoid common triggers: Cut out obvious offenders like fermented foods, aged meats, pickled vegetables, MSG, artificial colors/preservatives, and cortisol-stimulating ingredients.
Include DAO-boosting foods: Eat plenty of foods high in diamine oxidase (DAO) such as asparagus, spinach, broccoli, parsley, banana, oats, ginger, turmeric, licorice root, and kidney beans. DAO helps break down histamines.
Maintain balance with MAO and putrescine: Also get enough foods containing monoamine oxidase (MAO) such as spinach, Swiss chard, and white beans plus putrescine like cabbage, cauliflower, and prunes. These enzymes help regulate excess amino acids that convert to histamine.
Choose fresh, hypoallergenic options: When possible, select fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, grilled meats, and simply prepared snacks and meals. Hypoallergenic recipes minimize potential histamine triggers.
Stay properly hydrated: Drink plenty of purified water and herbal teas throughout the day to support detoxification and digestion. Too little water impairs the body’s ability to handle histamines effectively.
Consider supplements if needed: Vanilla extract, peppermint or ginger capsules may soothe the digestive tract. DAO, bromelain, betaine HCL, and digestive enzymes can boost specific enzymes involved in histamine metabolism.
Eat three meals and two snacks per day: Having regular, balanced meals prevents dips in blood sugar that trigger histamine release while skipping meals. But do not overeat.
DAO Foods: The Key to Histamine Intolerance Relief
What you eat has a significant impact on your ability to handle histamines properly. Focusing on foods that naturally boost diamine oxidase (DAO), the main enzyme responsible for degrading dietary histamines, is key to managing intolerance and gaining relief from symptoms. Some of the top DAO-rich foods include:
| Food | Description |
| Grass-fed beef, chicken, pork, and lamb | These foods contain high amounts of DAO enzymes and amino acids needed to produce them, helping ensure adequate breakdown of histamines from meat consumption. |
| Salmon, sardines, and trout | Fatty fish are delicious sources of omega-3 fats and also provide DAO enzymes. The fat helps with absorption. |
| Eggs, especially egg yolks | Eggs contain many of the cofactors needed to support DAO production and activity, making them a part of a balanced histamine diet. |
| Kale, spinach, Swiss chard, and collard greens | These leafy greens are nutritional powerhouses boasting folate, vitamin C, and minerals which aid DAO production and help offset high-histamine foods. |
| Asparagus | Asparagus is high in enzymes and amino acids specifically needed to break down histamines, making it a good source of natural DAO enzymes. |
| Broccoli | Glucosinolates in broccoli boost DAO levels and help modulate inflammation, improving the body’s ability to handle excess histamines. |
| Kidney beans, lima beans, and lentils | Beans and lentils provide fiber, protein, B vitamins and minerals supporting DAO enzyme activity and gut health. |
| Olive oil | Rich in monounsaturated fats, especially oleic acid, which helps with absorption and transport of DAO enzymes throughout the body. |
| Turmeric, ginger, oregano, rosemary, thyme, and peppermint | These herbs and spices have natural anti-inflammatory effects and support digestion, improving histamine metabolism. |
| Bananas | Bananas are high in prebiotics, potassium, vitamin B6, and tryptophan, which aid gut bacteria balance, inflammation control, and DAO enzyme production. |
Additional Strategies for Managing Histamine Intolerance
Here are a few additional strategies that can help support managing histamine intolerance:
- Supplement with digestive enzymes and DAO: For those with impaired enzyme production or activity, supplements may help improve digestion and histamine breakdown. Look for diamine oxidase or DAO formulas in particular.
- Maintain gut health with probiotics: A balanced microbiome is critical for coping with excess histamines. Probiotics containing Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains promote gut barrier integrity and enzyme production.
- Detoxify and reduce inflammation: Use herbs and supplements like peppermint, turmeric, boswellia, glutathione, alpha lipoic acid and NAC to decrease inflammation and remove histamine- production triggers.
- Control exposure to Imidazole acetaldehyde: This toxic byproduct of histamine metabolism can cause vasodilation, itching, and rashes. Limit heating meats at high temperatures and exposure to cigarette smoke.
- Calm hyperactive mast cells: Mast cell stabilizers or H1/H2 blockers may provide relief for those with mast cell activation syndrome. Only use under medical guidance as they can induce symptom dependence over time.
- Manage excess histamine toxicity: Be sure to stay properly hydrated, get enough salt, and use lactic acid bacteria or DAO supplements. In extreme cases, hospitalization and emergency treatment may be needed until metabolism improves.
- Practice stress reduction: Too much cortisol, the stress hormone, can drive inflammation and release of histamine. Yoga, meditation, deep breathing, massage therapy or other relaxing techniques help keep stress in check.
- Consider medical tests and procedures: If diet and natural strategies do not adequately control symptoms, blood tests checking histamine levels and DAO function may help determine if prescription medication could provide added benefit. Candida treatments, parasite removal or IVIG may also sometimes apply.
Additional medical guidance should always precede the use of stronger interventions. The strategies discussed here can help boost your symptoms and provide more relief when combined with a histamine-reduced diet focused on DAO-rich, nutrient-dense foods.
| Don’t let histamine intolerance control your life. Book a visit with SeeBeyond Medicine to learn about the benefits of DAO Foods and start feeling better. |
Conclusion
Eating foods that boost diamine oxidase (DAO) levels is one of the most effective strategies for managing histamine intolerance symptoms. By increasing your body’s ability to properly break down excess histamines, you can significantly reduce uncomfortable side effects and improve your quality of life.
Some of the key benefits of focusing on DAO foods include:
- Lowered histamine levels. DAO foods provide the nutrients and enzymes needed to support adequate histamine degradation. This helps prevent excess buildup of histamine in the body.
- Decreased histamine release. DAO foods promote balanced enzyme production and gut health, reducing inappropriate histamine release that leads to symptoms.
- Calmer histamine receptors. With stable histamine levels maintained through a diet rich in DAO foods, histamine receptors stay less sensitive and irritated, resulting in an absence of symptoms.
- Improved digestion. DAO foods strengthen digestion and the immune system, allowing food intolerances and sensitivities to lessen or disappear over time. Digestion issues often root underlying excess histamine production.
- Reduced inflammation. Many DAO foods have anti-inflammatory effects, which helps limit excess histamine from triggering inflammation in the first place or worsening symptoms of inflammation-related conditions.
- Control of underlying conditions. Eating DAO foods may help manage related conditions like SIBO, allergies, autoimmunity or adrenal insufficiency that can contribute to histamine intolerance symptoms by promoting gut balance, immunity support, and toxin removal.
Experience Relief from Histamine Intolerance with SeeBeyond Medicine Clinic’s Integrative Care
For those struggling with discomforts of histamine intolerance, consulting with doctors at SeeBeyond Medicine who specialize in integrative care is highly recommended.
We can evaluate your unique condition, run tailored tests when needed, and provide treatment plans focused on both dietary and natural therapeutic strategies to help you achieve relief and vibrant health.With patience, determination, and consistent application of expert recommendations, managing histamine intolerance is absolutely possible. DAO foods are a critical first step, but medical guidance can help you address other underlying factors supporting your symptoms as well.
