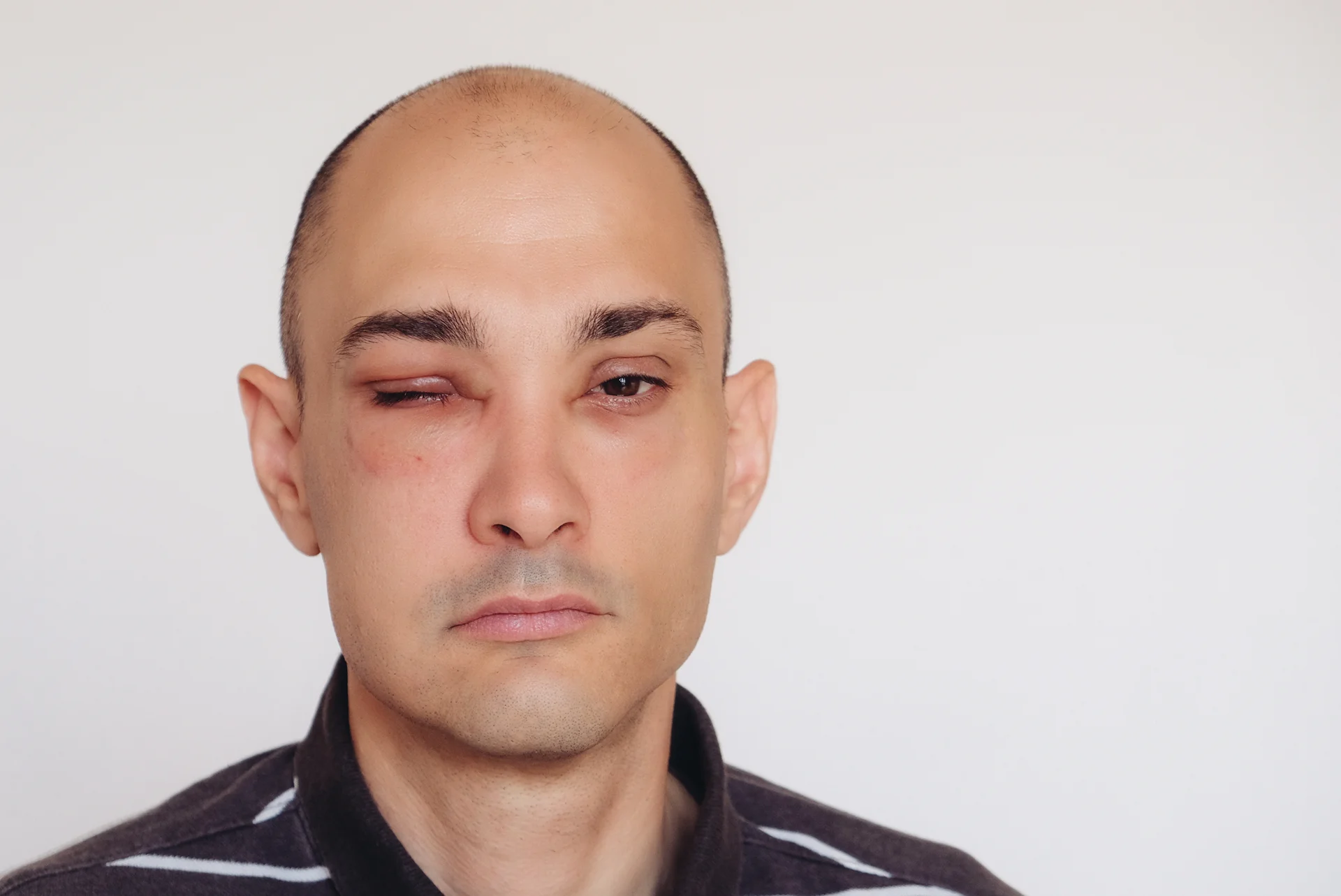
The Role of Histamine in Angioedema and the Potential Impact of DAO Deficiency
Acquired angioedema is a condition characterized by sudden swelling in the deeper layers of the skin, often in the face, limbs, throat, and intestinal tract. Attacks of angioedema can be disfiguring and painful, and swelling in the throat can potentially block airways. While the exact cause is unknown, angioedema is linked to having higher than normal levels of histamine – a chemical in the body involved in immune responses and regulating stomach acid.
Histamine is released by specialized white blood cells and binds to receptors on cells, causing effects like inflammation, itchiness, mucus production, and smooth muscle contraction. Though histamine has important roles in the body’s immune defenses and physiological functions, elevated levels can lead to adverse reactions like hives, swelling, and digestive issues.
Understanding histamine’s involvement is key to unraveling acquired angioedema.
Understanding DAO Enzyme Deficiency and Histamine Intolerance
An enzyme called diamine oxidase (DAO) helps regulate histamine levels by breaking it down. DAO deficiency leads to an accumulation of circulating histamine. This manifests in symptoms like hives, headaches, digestive discomfort, and possibly angioedema attacks.
When DAO activity is insufficient, histamine cannot be effectively metabolized after it is released. As a result, concentrations in the blood and tissues rise. Though studies on this matter are few, DAO deficiency is suspected to be a key driver of histamine intolerance.
Histamine intolerance is characterized by excess levels of histamine in the body. This can occur when the enzymes responsible for breaking down histamine are unable to keep up with histamine production or intake through food.
The inability to properly metabolize histamine can lead to a variety of symptoms including headaches, digestive distress, irregular menstrual cycles, tissue swelling, dizziness, and problems regulating body temperature. The root cause is an imbalance between histamine production and degradation, not an allergy or sensitivity to histamine itself.
Foods high in histamine like aged cheeses, wine, processed meats, and fermented foods can trigger symptoms in those with histamine intolerance. The main treatment focuses on following a low-histamine diet and possibly supplementing with histamine-lowering probiotics or enzymes.
Chronic Urticaria and Its Clinical Symptoms
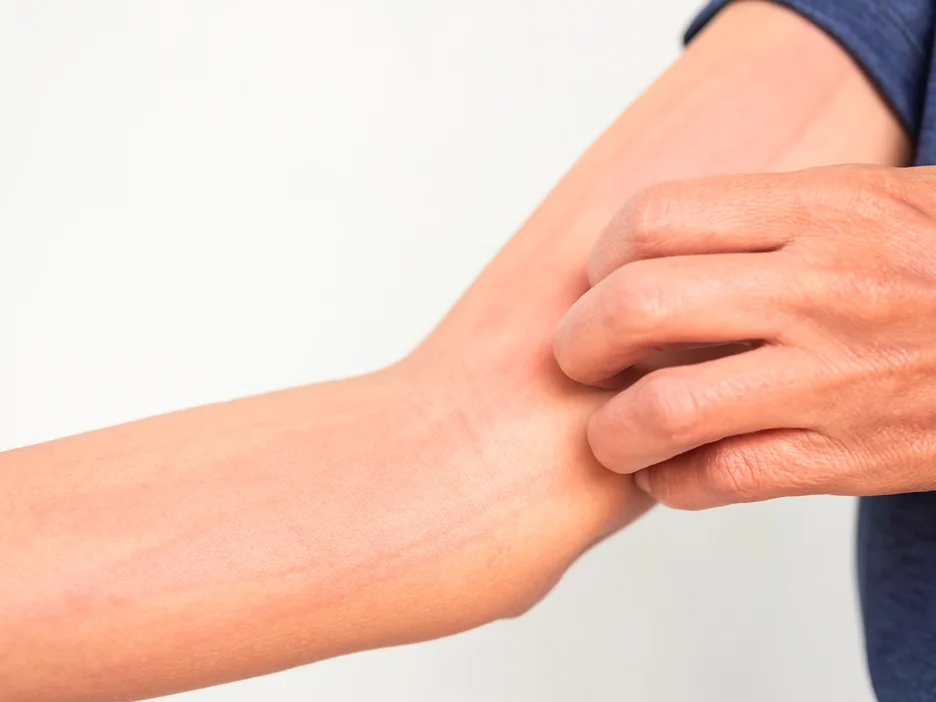
Chronic hives or urticaria is linked to angioedema, with both often resulting from histamine release. In chronic urticaria, histamine induces swelling and red, itchy wheals on the skin. Spontaneous urticaria arises on its own, while idiopathic urticaria has no known cause. Though mast cells activated to release histamine are the primary driver, the root triggers differ between patients.
For some, urticaria results from autoimmune disorders or allergic reactions to foods, medications, insect stings, and latex. For others, pseudoallergic reactions, stress, infections, hormones, sunlight, pressure, or exercise provoke symptoms.
Determining the subtype and triggers of urticaria is key to proper treatment. Antihistamines help control symptoms regardless of the cause.
The Connection Between Allergic and Pseudoallergic Reactions
True allergic reactions involve the immune system detecting an allergen and mounting an IgE antibody response, which then activates mast cells. Common allergic conditions like atopic dermatitis, asthma, and food allergies stem from this process. Pseudoallergic reactions also stimulate histamine release through mast cell degranulation. However, antibodies are not involved.
Instead, factors like temperature, pH changes, immune complexes, medications, food chemicals, and stress act directly on mast cells, signaling them to release mediators. Both true allergic reactions and non-allergic pseudoallergic reactions can drive chronic urticaria and angioedema by elevating histamine.
Dietary Considerations for Patients with Histamine Intolerance
For those with suspected histamine intolerance related to DAO deficiency, dietary changes may provide relief by limiting histamine intake. Many foods naturally contain histamine or may release it from mast cells upon digestion.
A low-histamine or histamine-free diet focuses on fresh, unprocessed foods. Foods particularly high in histamine like aged cheese, fermented foods, processed meats, sauerkraut, and red wine are avoided. Allergenic foods, alcohol, and gut irritants may also worsen symptoms. An elimination diet trial helps determine personal triggers. Improving gut health through probiotics and gentler foods may also aid digestion.
Additionally, here are other foods that you should and shouldn’t eat to regulate your histamine level naturally:
| Foods to Eat | Foods to Avoid |
| Fruits and vegetables like lettuce, carrots, pears, and berries | Vinegar-containing foods like dressings and sauces |
| Fresh meats and certain fresh or frozen fish like salmon and tuna | Nightshade vegetables like tomatoes, eggplant, and peppers |
| Eggs including quail eggs | Citrus fruits, spinach, mushrooms, soybeans |
| – Most fresh herbs like parsley, basil, and oregano | Bananas, nuts, chocolate, cocoa, wheat germ |
| Foods high in vitamin C like broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage, and sweet potatoes | Canned and pickled foods |
| Probiotics to support gut bacteria | Yeast extract, mate tea, energy drinks |
| Quercetin-rich foods like onions, broccoli, grapes, and green tea |
Therapeutic Options for Managing Symptoms
Currently, no standardized therapeutic protocols exist for treating histamine intolerance. Antihistamines provide temporary relief of acute urticaria and angioedema but do not resolve underlying DAO deficiency if present. Long-term antihistamine use also has drawbacks like sedation and tolerance.
Measuring serum DAO activity could identify individuals who may benefit from DAO enzyme supplements to break down excess histamine. However, clinical trials are still needed to establish efficacy and dosage guidelines. Restricting dietary histamine also offers a non-drug approach. Multimodal lifestyle changes, trigger avoidance, and targeted treatments tailored to the individual provide the best outcomes.
Subgroups of Patients and Specific Conditions
Though acquired angioedema is distinguished by occurring later in life with no family history, it shares the hallmark of elevated histamine with hereditary angioedema. HAE stems from a genetic mutation affecting regulation of bradykinin rather than histamine. However, histamine likely contributes to symptoms in both forms.
Mast cell activation syndrome (MCAS), migraines, and dermatographia are additional examples of conditions where histamine intolerance may play a role. MCAS in particular mirrors symptoms of idiopathic anaphylaxis and involves recurrent mast cell degranulation episodes. Reducing histamine levels through enzyme therapy, mast cell stabilizers, and diet could provide relief across these conditions.
Conclusion
In summary, histamine signaling appears to be implicated in acquired angioedema and related disorders marked by hives, swelling, and mast cell mediator release. Though more research is needed, managing histamine levels through dietary changes, antihistamines, and addressing underlying DAO deficiency may provide symptom relief and improved disease outcomes. As our understanding of histamine intolerance grows, more targeted treatment approaches are on the horizon.
Try DAO-HIST Today for Histamine Support

If you experience symptoms of histamine intolerance like swelling, digestive issues or headaches, DAO-HIST supplements from SeeBeyond Shop may help.
DAO-HIST supplements provide diamine oxidase, an important enzyme that breaks down histamine in the body. By supporting healthy histamine levels, DAO-HIST may reduce symptoms associated with conditions like angioedema, chronic hives, migraines and more.
Book your free consultation online to learn more about DAO-HIST and try it yourself!